Clean Water Initiative
Summary of Water Quality : Physico-chemical parameters and Fish fauna studies of Chichghat forest valley ponds to determine quality of water.
|
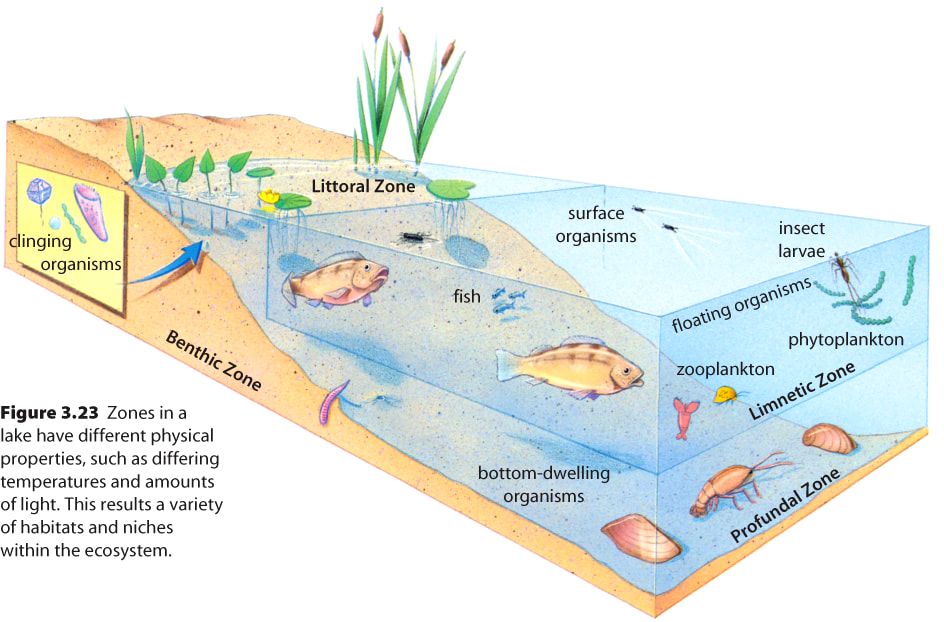
Planktonic studies are very useful tool for assessment water quality in any type of water body. Physical and chemical parameters are studied to ascertain the health of water body. Phytoplankton constitute the first tropic level. They play an important role as food for herbivorous animals especially the fish.
Phytoplankton are autotrophic (self feeding components of the plankton community) and a part of ocean, seas and freshwater basin ecosystem. They are agents for “primary production” , the creation of organic compound from carbon dioxide dissolved in the water, a process that sustains the aquatic food web . |
Indian Glass fish ( Ambassis ranga)
|
|
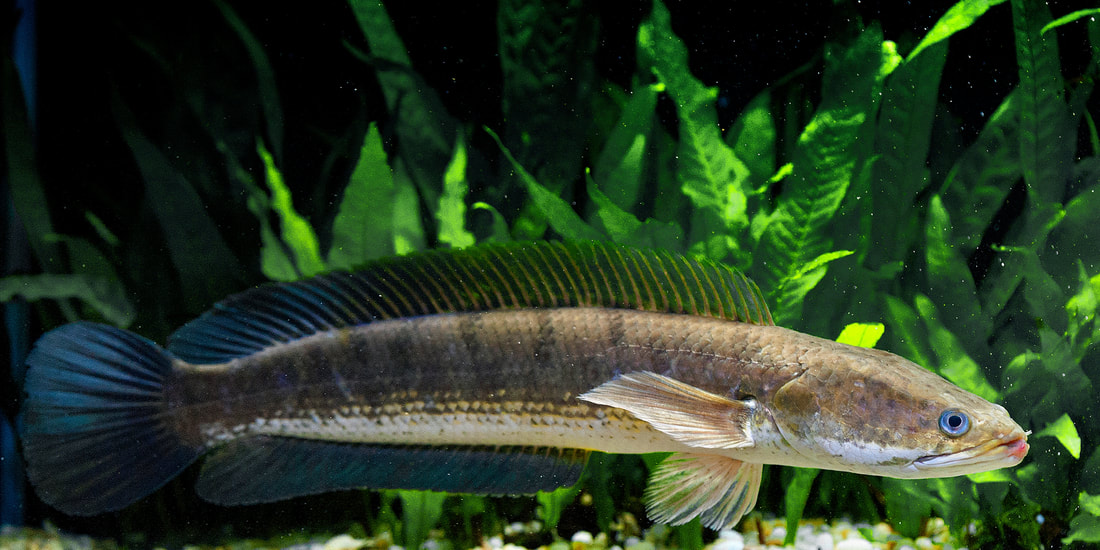
The Striped Snakehead ( Channa striata )
|
Zooplankton act as a primary and secondary links in food chain. The zooplankton communities are influenced by biological interactions, predation and interspecific competition for food resources. Seasonal fluctuation of zooplankton is governed by abiotic and biotic factors.
Fine detritus (dead plankton) suspended in the pelagic zone is colonized by heterotrophic bacteria, which is then consumed by protists (ciliates and flagellates) and generalist grazers. The protists in turn are consumed by other protists or by copepods. |
This return of energy to the pelagic food chain is called the ‘microbial loop’. Other detritus produced in the epilimnion may be trapped at the thermocline or sink into the hypolimnion where it is decomposed by bacteria.
Grazing zooplanktons are consumed by predatory invertebrates (rotifers, cyclopoid copepods, some cladocerans and insect larvae of the genus Chaoborus) or vertebrates (typically fish). Zooplanktivorous fish also consume predatory invertebrates. In turn, the zooplanktivorous fishes are consumed by Piscivorous fishes which sit atop the natural food webs of most lakes.
Grazing zooplanktons are consumed by predatory invertebrates (rotifers, cyclopoid copepods, some cladocerans and insect larvae of the genus Chaoborus) or vertebrates (typically fish). Zooplanktivorous fish also consume predatory invertebrates. In turn, the zooplanktivorous fishes are consumed by Piscivorous fishes which sit atop the natural food webs of most lakes.
A total 15 Species of Fish and 35 species phytoplankton and zooplankton belonging to four groups viz. Chlorophyceae (19 species), Bacillariophyceae (06 species), Myxophyceae (08 species) and Euglenophyceae (02 species) representing phytoplankton diversity was observed. The year on year study across all three seasaons shows, maximum phytoplankton density recorded during winter season and this is due to low ambient temperature. It is thus evident that these ponds can support biota and are not polluted by pollutants or sewage.
Research conducted by PhD Students of Nagpur University Fisheries department of under the guidance of their guide and Head of Department, Dr. Vidya Baile, revealing a substantial rise in phytoplankton and fish species over the years.